Quick Understanding of Diamond Grading Standards
You may have heard of the 4C grading standards for diamonds.
So, what are the 4Cs of diamonds?
What are the authoritative institutions for diamond grading?

What is the 4Cs of diamond quality?
Beautiful. Rare. Cherished. Each diamond is unique and is a miracle of time, place and change. And each has specific qualities that establish its value.
Until the middle of the twentieth century, there was no agreed-upon standard by which diamonds could be judged. GIA created the first, and now globally accepted standard for describing diamonds: Color, Carat, Clarity and Cut. Today, the 4Cs of Diamond Quality is the universal method for assessing the quality of any diamond, anywhere in the world.
-

COLOR
Diamond color actually means lack of color.
Understanding what diamond color means helps in choosing the right diamond. Interestingly, the diamond color evaluation of most gem-quality diamonds is based on the absence of color.
A chemically pure and structurally perfect diamond has no hue, like a drop of pure water, and consequently, a higher value.
GIA’s D-to-Z diamond color-grading system measures the degree of colorlessness by comparing a stone under controlled lighting and precise viewing conditions to masterstones of established color value.
-
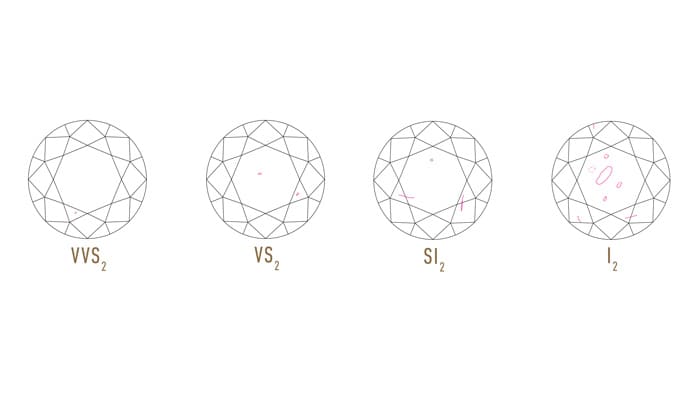
CLARITY
Diamond clarity refers to the absence of Inclusions and blemishes.
The GIA Diamond Clarity Scale has 6 categories, some of which are divided, for a total of 11 specific grades.
- Flawless (FL): No inclusions and no blemishes visible under 10x magnification.
- Internally Flawless (IF): No inclusions visible under 10x magnification.
- Very, Very Slightly Included (VVS1, VVS2): Inclusions so slight they are difficult for a skilled grader to see under 10x magnification.
- Very Slightly Included (VS1, VS2): Inclusions are observed with effort under 10x magnification, but can be characterized as minor.
- Slightly Included (SI1, SI2): Inclusions are noticeable under 10x magnification.
- Included (I1, I2, I3): Inclusions are obvious under 10x magnification which may affect transparency and brilliance.
-
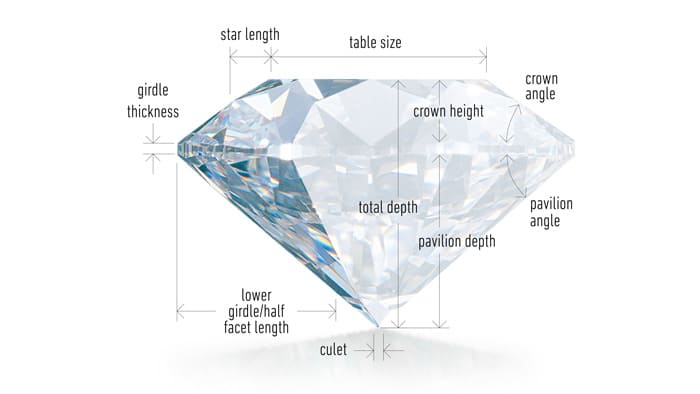
CUT
The cut of a diamond needs to be assessed from many dimensions.
Diamonds are renowned for their ability to transmit light and sparkle so intensely. We often think of a diamond’s cut as shape (round, heart, oval, marquise, pear), but what diamond cut actually does mean how well a diamond’s facets interact with light.
Cut is rated on a scale of Poor to Excellent, and is mesured by three primary factors: brightness, fire and scintillation. GIA’s diamond cut grade also takes into account the design and craftsmanship of the diamond, including its weight relative to its diameter, its girdle thickness (which affects its durability), the symmetry of its facet arrangement, and the quality of polish on those facets.
-

CARAT WEIGHT
Diamond carat weight measures a diamond’s apparent size.
To put it simply, diamond carat weight measures how much a diamond weighs.
A metric "carat" is defined as 200 milligrams. Each carat is subdivided into 100 "points". This allows very precise measurements to the hundredth decimal place. A jeweler may describe the weight of a diamond below one carat by its "points" alone. We may refer to a diamond that weighs 0.25 carats as a "twenty-five pointer". Diamond weights greater than one carat are expressed in carats and decimals. A 1.08 carat stone would be described as "one point and eight carats".
All else being equal, diamond price increases with diamond carat weight because larger diamonds are rarer and more desirable. However, two diamonds of equal carat weight can have very different values (and prices) depending on three other factors of the diamond 4Cs: Color, Clarity and Cut.
While now you know what carat means, it’s also important to remember that a diamond’s value is determined using all of the 4Cs, and not just carat weight.

International authoritative diamond appraisal institutions
There are many international diamond and jewelry appraisal institutions, but the five most well-known and widely recognized ones are:
- the Gemological Institute of America (GIA)
- the High Diamond Council in Belgium (HRD)
- the American Gem Society (AGS)
- the International Gemological Institute (IGI)
- and the European Gemological Laboratory (EGL)
Over two-thirds of diamonds worldwide are assessed by these laboratories, and the certificates they issue are highly authoritative and internationally acknowledged.
We provide quality-assured natural diamonds.
Diamonds of 0.30 carats and above used in ZWonder jewelry pieces come with certificates from internationally authoritative diamond appraisal institutions.




